How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate data collection. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to mastering drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, delve into safe flying practices, and equip you with the knowledge to capture stunning visuals.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will empower you to confidently take to the skies.
Understanding the intricacies of drone technology is crucial for safe and responsible operation. This guide breaks down complex concepts into manageable steps, ensuring you grasp the fundamentals before progressing to more advanced techniques. We’ll examine various flight modes, camera settings, and maintenance procedures, providing you with a solid foundation for your drone piloting journey. By the end, you’ll be well-prepared to navigate the airspace responsibly and creatively.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of your drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section details the major components and their functions, as well as explores variations in key elements like propellers and batteries.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive guidance. From there, practice and familiarization with your specific drone model will further enhance your skills and ensure safe and efficient operation.
Drone Component Functions
A typical drone consists of several key components working in harmony. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and maneuver. Different propeller designs influence flight characteristics.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Their power and efficiency directly impact flight time and maneuverability.
- Flight Controller: This is the drone’s “brain,” processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands from the remote controller. It’s responsible for keeping the drone level and stable in the air.
- Battery: The power source for the entire drone system. Battery capacity and type significantly affect flight duration.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Used for positioning and navigation, enabling features like autonomous flight and return-to-home functionality. It provides precise location data to the flight controller.
- Camera: Captures images and videos, offering a bird’s-eye perspective. Camera quality and features vary greatly depending on the drone model.
Drone Propeller Types and Their Impact
Drone propellers come in various designs, each impacting flight performance differently. Key factors include size, pitch, and material. Larger propellers generally generate more thrust, while a higher pitch results in faster speed but potentially reduced maneuverability. Materials such as nylon or carbon fiber affect durability and weight.
Battery Types Comparison
Different battery types offer varying performance characteristics. The choice depends on factors like flight time requirements, weight considerations, and budget. Here’s a comparison of common types:
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Flight Time (approx.) | Weight (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | 7.4 – 22.2 | 15-30 minutes (varies greatly by drone and battery capacity) | 50-500g (varies greatly by capacity) |
| LiFe (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | 3.2 – 14.8 | Similar to LiPo, but often slightly less | Slightly heavier than LiPo for same capacity |
| LiHV (High Voltage LiPo) | 8.4 – 25.2 | Slightly longer than standard LiPo | Similar weight to LiPo |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage. This section details the essential steps to ensure a safe and successful flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist should include the following:
- Battery Check: Verify battery charge level is sufficient for the planned flight time. Ensure the battery is securely connected.
- Propeller Inspection: Check for any damage or looseness on the propellers. Replace damaged propellers immediately.
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Ensure the drone has a strong GPS signal before takeoff. This is crucial for accurate positioning and safe flight.
- Calibration: Perform any necessary sensor calibrations as recommended by the drone manufacturer.
- Remote Controller Check: Verify that the remote controller is fully charged and properly connected to the drone.
- Surrounding Environment Assessment: Inspect the area for obstacles, people, and potential hazards. Ensure you have a clear and safe flight path.
Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation requires strict adherence to several crucial safety procedures. These are designed to minimize the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Maintain Safe Distances: Keep the drone at a safe distance from people, buildings, and other obstacles. Never fly over crowds or unauthorized areas.
- Observe Airspace Restrictions: Familiarize yourself with local airspace regulations and restrictions before flying. Many areas have designated no-fly zones.
- Avoid Flying in Adverse Weather: Do not fly in strong winds, rain, snow, or fog. Adverse weather conditions can significantly impact drone stability and control.
- Visual Line of Sight: Always maintain visual contact with the drone during flight. Never fly beyond your visual range.
Safe Drone Launch and Landing Sequence
A systematic approach to launching and landing is crucial for safety. The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved:
[Imagine a flowchart here showing: Power on drone & controller -> Check battery & GPS -> Pre-flight checks -> Select flight mode -> Takeoff (smooth ascent) -> Flight maneuvers -> Smooth descent -> Landing (gentle touchdown) -> Power off drone & controller]
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
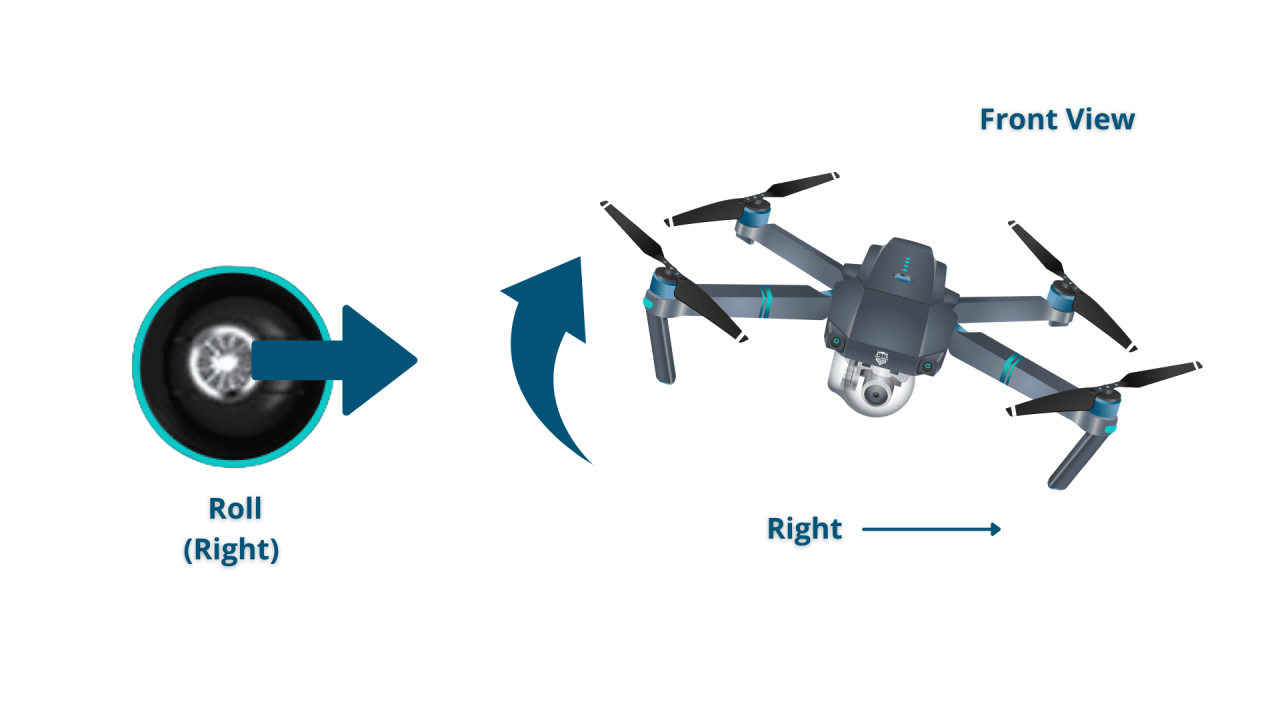
Understanding the basic flight controls and maneuvers is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section explains the functions of the remote controller and demonstrates how to perform basic flight operations.
Remote Controller Functions
Most drone remote controllers use two joysticks (or thumbsticks) and several buttons. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls forward/backward and left/right movement. Buttons often control camera functions, flight modes, and return-to-home.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering these maneuvers is crucial for safe and controlled flight:
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards to initiate a smooth and controlled ascent.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air by carefully adjusting the left stick to control altitude.
- Forward/Backward Movement: Use the right stick to move the drone forward or backward.
- Sideways Movement: Use the right stick to move the drone left or right.
- Rotation (Yaw): Use the left stick to rotate the drone clockwise or counterclockwise.
Smooth and Controlled Landing

A smooth landing prevents damage to the drone and ensures safety. Follow these steps:
- Begin a slow descent by gently lowering the left stick.
- Maintain a stable hover just above the landing area.
- Slowly lower the drone until it touches down gently.
- Power off the drone and remote controller.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, exploring advanced flight techniques enhances your drone piloting skills and opens up creative possibilities. This section covers flight stability, various flight modes, and their comparative advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge; a great resource for learning is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , covering everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology and relevant rules.
Flight Stability and Maintenance
Maintaining flight stability is crucial, especially in windy conditions or complex environments. Factors like wind speed, air pressure, and even battery level can affect stability. Practice smooth control inputs and learn to compensate for external factors.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and autonomy:
| Flight Mode | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS Mode | Uses GPS for positioning and stabilization. | Stable flight, easier control, features like return-to-home. | Requires a strong GPS signal, less precise control in GPS-denied environments. |
| Attitude Mode | Maintains orientation relative to the pilot’s perspective. | More precise control, works even without GPS. | Less stable, requires more piloting skill. |
| Manual Mode | Direct control over all aspects of flight. | Maximum control, ideal for experienced pilots. | Requires significant skill, higher risk of accidents. |
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of many drones, enabling stunning aerial photography and videography. This section explores camera settings and techniques for capturing high-quality images and videos.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Understanding camera settings like resolution, ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is crucial for optimal image quality. Higher resolution results in larger file sizes but better detail. ISO affects sensitivity to light, while shutter speed and aperture control exposure and depth of field.
Optimal Image Stabilization
Achieving stable images and videos is essential for professional-looking results. Many drones offer electronic image stabilization (EIS) or mechanical gimbal stabilization. Smooth, controlled flight also minimizes camera shake.
Capturing Different Types of Shots
Drones allow for creative shot types, including:
- Aerial Photos: Capture stunning overhead views of landscapes and buildings.
- Videos: Create dynamic footage showcasing movement and perspective.
- Time-lapses: Capture the evolution of a scene over time.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and the ability to troubleshoot common problems are vital for keeping your drone in top condition and extending its lifespan. This section covers routine maintenance tasks and solutions for common issues.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance includes:
- Cleaning propellers and body after each flight.
- Inspecting for physical damage.
- Properly storing the battery.
- Checking for loose screws or connections.
- Calibrating sensors periodically.
Common Drone Problems and Causes
Some common problems and their potential causes include:
- Low Battery Warnings: Low battery charge.
- GPS Signal Loss: Obstructions, interference, or weak signal.
- Motor Malfunctions: Damaged motor, loose connections, or low battery.
- Unstable Flight: Calibration issues, damaged sensors, or wind conditions.
Troubleshooting Steps
Troubleshooting involves systematically checking components and addressing potential issues. Consult the drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. This section Artikels key legal considerations and best practices for responsible drone operation.
Relevant Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Check with your local aviation authority for specific rules regarding airspace restrictions, registration requirements, and operational limitations.
Respecting Privacy and Avoiding Unauthorized Surveillance
It’s crucial to respect the privacy of others and avoid unauthorized surveillance. Never fly over private property without permission and be mindful of recording individuals without their consent.
Best Practices for Responsible Drone Operation
Responsible drone operation involves:
- Flying only in designated areas.
- Maintaining visual line of sight.
- Adhering to all local regulations.
- Respecting the privacy of others.
- Flying safely and responsibly.
Illustrative Example: Flight Path Planning

Planning a complex flight path requires considering various factors to ensure a safe and successful flight. This section illustrates a scenario involving obstacle avoidance and specific maneuvers.
Complex Flight Path Scenario
Imagine a flight path around a building with trees and a pond. The drone needs to ascend to 50 feet, navigate around the building (100 feet x 100 feet), avoid three trees (each 20 feet in diameter), and then land near the starting point.
Flight Path Planning Steps
Planning this flight involves:
- Assessing the environment and identifying obstacles.
- Determining a safe altitude and flight path.
- Considering wind conditions and their impact on flight.
- Calculating the required battery life for the planned flight duration.
- Creating a visual representation of the flight path (using a map or software).
Textual Flight Path Description, How to operate a drone
The drone takes off and ascends to 50 feet. It then moves North for 50 feet to clear the building. It turns East, circumnavigating the building (100 feet along the East side, then 100 feet along the South side). It then moves North to avoid a tree (20 feet diameter), adjusting its path slightly. Continuing North, it avoids another two trees, similarly adjusting its path to maintain a safe distance (at least 20 feet).
Finally, it turns West and descends for landing near the starting point.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical understanding and responsible practice. This guide has provided a framework for safe and effective drone piloting, covering pre-flight procedures, basic and advanced flight controls, camera operation, maintenance, and legal considerations. Remember, consistent practice and adherence to safety regulations are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. The skies await—explore them safely and responsibly.
FAQ Overview: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a ready-to-fly (RTF) drone with GPS stabilization and user-friendly controls is recommended. Look for drones with features like automatic return-to-home (RTH) and obstacle avoidance.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
It’s best to charge your drone battery after each flight. Avoid completely depleting the battery to prolong its lifespan.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (e.g., Attitude mode) and carefully bring it down. Avoid flying in areas with weak GPS reception.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by location. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.
